Why Your Ears Hurt After Swimming and What To Do
Most people ask: What causes ear pain after swimming? They are usually talking about the swimmer’s ear.
Bacteria cause this painful infection. When you are swimming, water gets inside your ears. Since the ear is warm, the water creates a warm and moist environment.
This is the kind of environment where bacteria thrive. They thrive there and cause you pain every time you swim.
Although it is called swimmer’s ear, even shower water getting into your ear can cause this infection. It can also develop from mild, to moderate to advanced if it goes untreated for a long time.
But water is not the only thing that causes swimmer’s ear. When you start putting hard things and cotton swabs in your ears, they damage the delicate skin of the eardrum. This can also cause a bacterial infection easily.
Also, check my article on: Can you swim with a cochlear implant?
Ear pain immediately after swimming
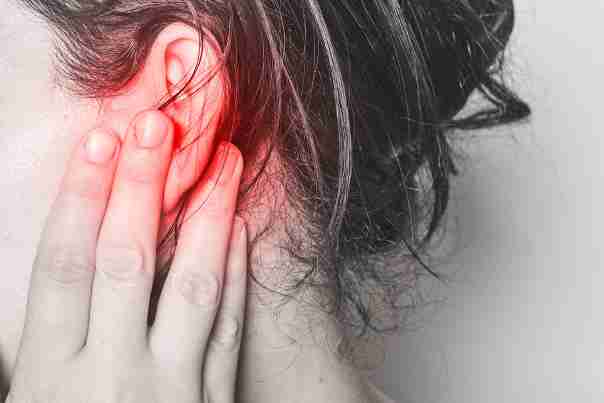

Ear pain immediately after swimming can be very concerning. It shows you that something is wrong. It can also prevent you from swimming.
The swimmer’s ear will occur in the outer canal. However, if you feel ear pain after swimming in cold water, it does not always mean you have a swimmer’s ear. Rather, it can also mean that you have an infection in the inner ear.
Thus, it would be better to know how to tell the difference between pain in the inner ear and pain in the outer ear after swimming.
So, how can you tell you have the swimmer’s ear and not an inner ear infection?
First, when you pull the ear lobe, you will feel the pain escalate. If that is the case, you have a swimmer’s ear. Since the infection occurs close to the ear opening, you feel more pain when you pull your earlobe.
Secondly, if the pain is inside the eardrum, that is, in the inner ear, the pain increases when you lie down, probably when the infected ear faces downwards.
Thus, in these two cases, you can see that it is possible to feel ear pain after swimming in the ocean or in the pool.
Thirdly, the symptoms of the outer ear infection are different from those of the inner ear infection. In this case, when you have a swimmer’s ear, you will notice the outer ear looking reddish, and it might also develop a rash.
If the inner ear is infected, you might experience a fever, vomiting, and even diarrhea. In both cases of the swimmer’s ear and the inner ear getting infected, you might get a discharge.
Ear pain after swimming – Main symptoms
In this section, we shall look at the symptoms that can show you that you have swimmer’s ear. They include the following:
One of the symptoms that you will experience with a swimmer’s ear is sore ears after swimming. This is not a strict kind of soreness. Rather, it is the kind of minimal soreness where you feel persistent itching from time to time in the ear canal.
If you start seeing drainage that is not smelly, you probably have a swimmer’s ear. Also, look out for redness in the ear.
However, for dark-skinned people, the redness might be hard to spot. If there is mild discomfort in the opening of the ear, you definitely have swimmer’s ear.
If you see the above water in ear symptoms, and do not get treatment, the condition is going to escalate.
Therefore, the symptoms can become a bit more advanced. You could start experiencing the following:
The itching from water in the ear becomes more intense, and you even start experiencing pain. There is also excess fluid coming from the ear.
Since the infected part starts to swell, you start experiencing a feeling of blockage. You can even stop hearing, especially with low-level sounds.
If you still do not get treatment, you could experience more trouble. One of the things you might start experiencing is fever, loss of hearing, serious pain on the side of the head with the affected ear, swelling of the side, and so on.
You should not let the situation escalate this much. You should see a doctor as soon as you realize that you have a swimmer’s ear.
Other Causes of Ear Pain During or After Swimming
Every kind of ear pain or discomfort that you experience after or during swimming is not always from the swimmer’s ear.
Here are the other conditions that might cause ear pain immediately after swimming:
My ear hurts after jumping into water
The ear can hurt after jumping into the water because of the changes in pressure. The cause of this pain and discomfort is called ear barotrauma.
The change in pressure in the water surrounding your body causes this pain. This also happens in aircraft when landing or taking off, due to the change in air pressure.
Ears hurt underwater
If you dive underwater, your ears might hurt. The reason for this is the difference in the pressure in your ears as well as that of the surrounding water.

However, this should be simple to correct. Pinch your nose and blow gently until your Eustachian tube is completely open.
If you feel ear pain after jumping into the pool, try this simple method. It will regulate the pressure in the ears to match the pressure of the water.
How to prevent water from entering your ears
When swimming in the ocean or in the pool, you can prevent water from entering your ears. Water from the two environments contains contaminants like bacteria, chlorine, salt, fungus, debris, and other types.
Since your ears are quite delicate, you want to keep all of this nasty stuff out of your ears. One of the ways to keep all of these things outside is to wear earplugs for swimming.
You might want to try the Hearprotek Upgraded Custom-fit Water Protection Adult Swimming earplugs that you can buy on Amazon.com.
Conclusion
The best thing to do after contracting the swimmer’s ear is to start treatment as soon as possible.
You can do this by using over-the-counter antibiotics, such as ibuprofen. But it is always best to go to the hospital to get a proper prescription to stop ear pain after swimming in the lake.
Also, the symptoms of ear pain after swimming are the same across the board: for both adults and children.